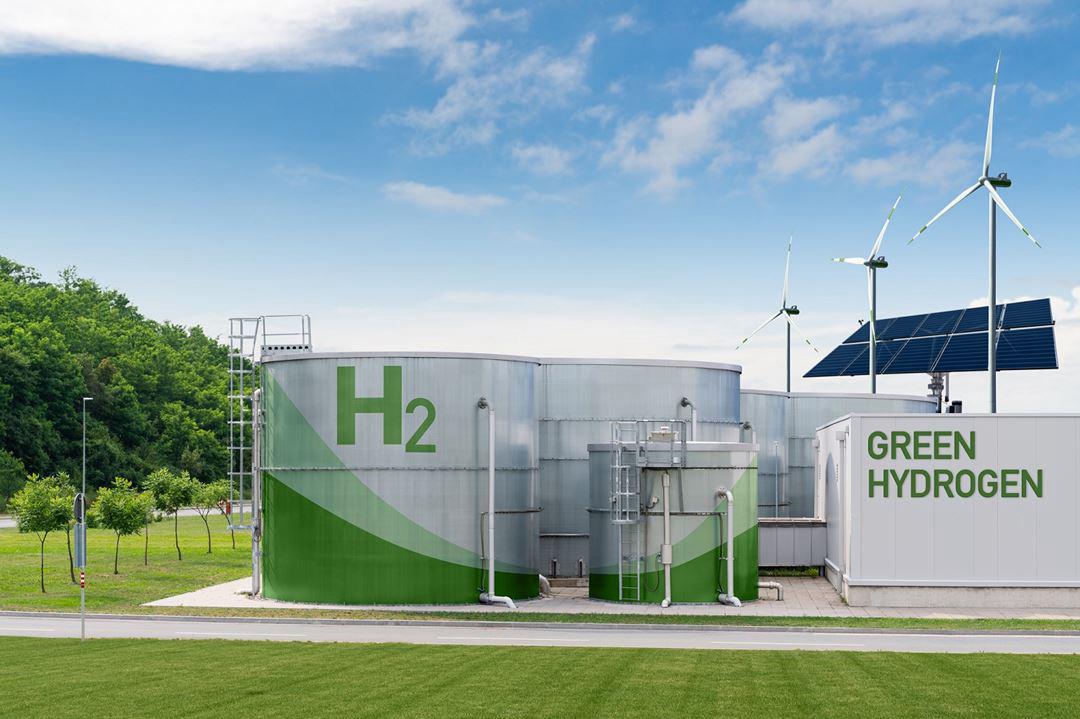
Low-carbon hydrogen is emerging as a game-changing energy resource that holds the potential to create a better environment and help countries achieve their carbon neutrality goals. As an element, hydrogen is a safe and clean source of energy that does not produce pollutants when burned. Its versatility makes it suitable for various applications, such as a source of heat for housing or a raw material in the industrial sector. Recently, it has gained attention as a future clean energy resource.
There are approximately 17 methods to produce low-carbon hydrogen, with each method emitting less than 2.4 kilograms of carbon dioxide for every one kilogram of hydrogen produced. Two of the most important types of low-carbon hydrogen are “green hydrogen” and “blue hydrogen.” Green hydrogen is produced using wind and solar-powered devices, while blue hydrogen is extracted from natural gas as a byproduct.
To gain insights into the potential of low-carbon hydrogen, KUNA interviewed several experts who shared their perspectives on this promising energy resource. Dr. Fotouh Al-Ragom, the Manager of the Energy Efficiency Technologies Program at the Kuwait Institute for Scientific Research (KISR), emphasized Kuwait’s keen interest in capitalizing on this opportunity. Dr. Al-Ragom highlighted Kuwait’s abundance of renewable natural resources, such as solar and wind energies, which could be utilized to produce green hydrogen not only for domestic consumption but also for export to other countries.
Dr. Al-Ragom pointed out that many countries worldwide are increasingly interested in low-carbon hydrogen as a viable energy resource. She also mentioned that Kuwait has taken significant steps towards achieving carbon neutrality by 2050 in the oil and gas sectors. This ambitious plan aligns with the goal of achieving total carbon neutrality for all sectors of the state by 2060. To reach this objective, Dr. Al-Ragom stressed the importance of reducing both direct and indirect carbon emissions. This can be achieved by minimizing the burning of gas in extraction and production operations and promoting a circular economy model that focuses on sharing, leasing, and reusing energy to reduce carbon emissions. Additionally, she highlighted the role of utilizing solar energy to produce electricity in further reducing carbon emissions.
Dr. Al-Ragom emphasized that Kuwait’s efforts align with the global commitment to renewable energy sources and efficiency, which aims to triple the use of such energy resources and decrease global temperatures by 1.5 degrees Celsius by 2030. Kuwait also aims to save 15 percent of its renewable energy needs by 2030, in line with the global pledge.
Discussing the usage of low-carbon hydrogen, Wael Abdulmotai, a natural gas industries expert at the Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC), mentioned that hydrogen is not a novelty and has been used in the past as a raw material in various industries. However, the current interest in hydrogen stems from its potential for future clean energy production. Abdulmotai acknowledged that there are obstacles to be addressed before widespread usage of low-carbon hydrogen can be realized.
One major concern is the high cost of producing low-carbon hydrogen, which is five times greater than producing natural gas. To fully harness the potential of low-carbon hydrogen, the necessary infrastructure must be developed to facilitate international commerce, similar to the infrastructure in place for oil and natural gas. Additionally, policies need to be devised to ensure the smooth organization of the production and distribution processes.
In conclusion, low-carbon hydrogen holds immense promise as a clean energy resource that can contribute to a sustainable future. Countries like Kuwait are actively exploring the utilization of renewable natural resources to produce low-carbon hydrogen, both for domestic consumption and international export. While there are challenges to overcome, such as cost and infrastructure development, the potential benefits of low-carbon hydrogen make it a worthwhile endeavor. By investing in this energy resource, countries can take significant strides towards achieving their carbon neutrality goals and creating a better environment for future generations.