Introduction to Current Weather Conditions in the Philippines
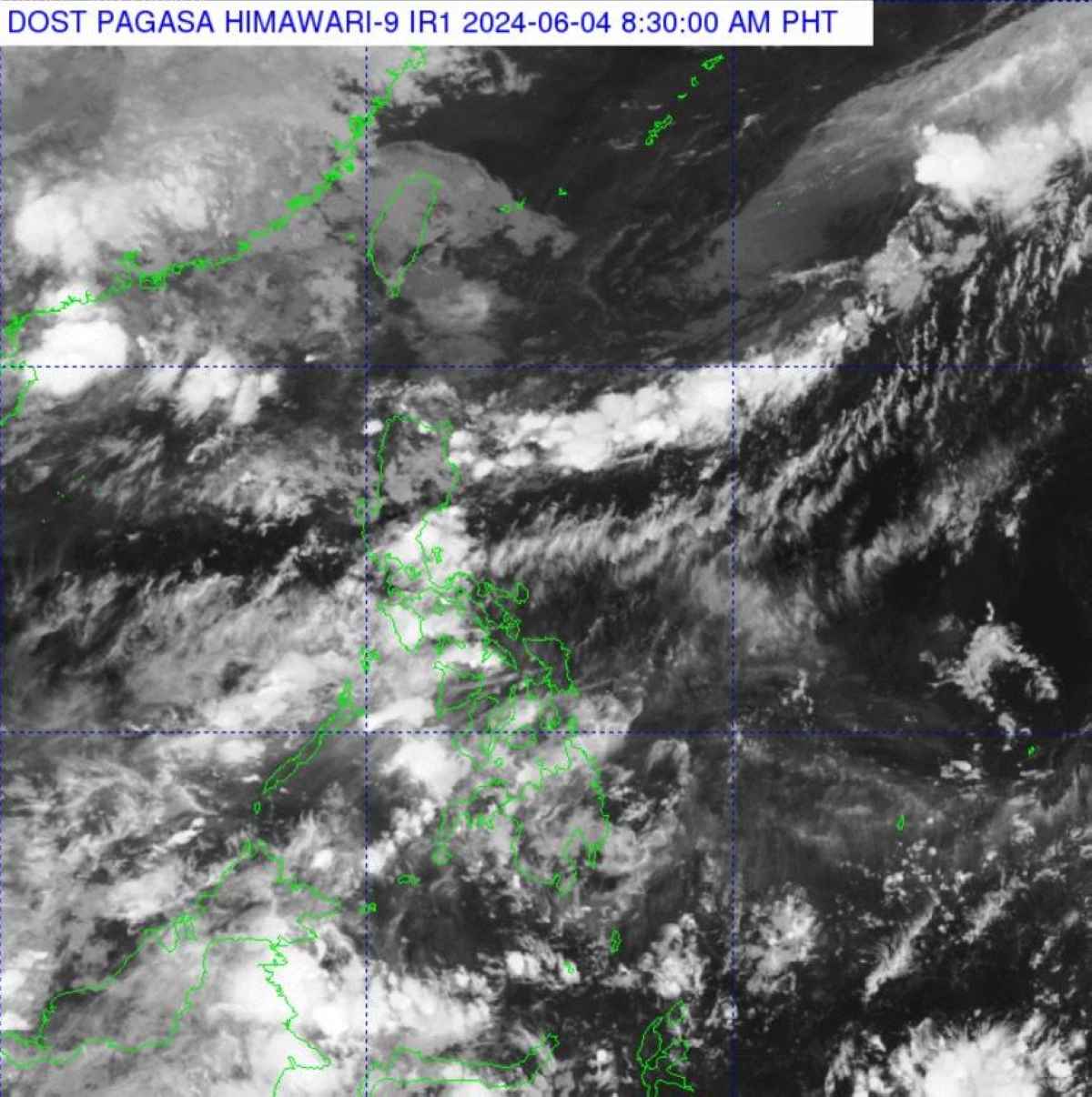
Recent updates from the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA) indicate notable weather patterns affecting the country. The northern regions of Luzon are currently experiencing significant cloud formations, attributed to a prevailing frontal system. This phenomenon often results in increased cloud cover and localized rainfall, impacting day-to-day activities and agricultural operations in these areas.
Conversely, the majority of the Philippines is facing hot weather conditions. Such temperature rises are typical during this time of year, contributing to heightened energy consumption due to increased use of cooling systems and presenting challenges to public health, particularly in urban centers where the heat island effect can exacerbate temperatures.
PAGASA, as the state-run weather authority, plays a crucial role in monitoring and forecasting these weather conditions. Utilizing advanced meteorological tools and satellite systems, PAGASA provides timely and accurate weather updates that are essential for disaster preparedness, agricultural planning, and public advisories. Their continuous surveillance and dissemination of weather information help mitigate the impacts of adverse weather events, ensuring the safety and well-being of the Filipino populace.
Understanding the dynamics of these weather patterns is essential for both short-term and long-term planning. The insights provided by PAGASA not only inform immediate actions but also contribute to broader climate studies and resilience-building efforts across the archipelago. As weather systems continue to evolve, the role of such agencies becomes increasingly critical in adapting to and mitigating the effects of climate variability in the Philippines.
The Role of the Frontal System in Weather Patterns
A frontal system is a meteorological phenomenon marking the boundary between two distinct air masses with varying temperature and humidity levels. These boundaries, often referred to as fronts, play a crucial role in shaping weather patterns by influencing the movement and interaction of air masses. In the Philippines, frontal systems significantly affect the weather, particularly in Northern Luzon, where they can lead to substantial changes in temperature, precipitation, and wind patterns.
One of the most common types of frontal systems in the region is the cold front. This occurs when a cold air mass advances towards a warmer air mass, forcing the warmer air to ascend. This upward movement often leads to the formation of clouds and precipitation, which can result in prolonged periods of rainfall and thunderstorms. For instance, during the Northeast Monsoon season, cold fronts frequently affect Northern Luzon, bringing cooler temperatures and increased rainfall to the area.
In contrast, a warm front forms when a warm air mass moves over a cold air mass. This interaction typically results in gradual temperature increases and more stable weather conditions. However, warm fronts can also bring extended periods of light rain and overcast skies as the warm air slowly rises above the cooler air. The influence of warm fronts is less pronounced in the Philippines compared to cold fronts but still contributes to the overall weather dynamics in the region.
When comparing these phenomena to other countries, the fundamental principles remain the same. In the United States, for example, the interaction between cold and warm fronts is a primary driver of the weather patterns observed in the Midwest and Northeast. Similarly, in Europe, frontal systems play a significant role in shaping the weather, particularly in the United Kingdom and Western Europe. Despite regional differences, the impact of frontal systems on weather patterns is a universal aspect of meteorology.
Understanding the role of frontal systems helps meteorologists predict weather changes more accurately, ultimately aiding in preparedness and response to varying weather conditions. For the Philippines, this knowledge is particularly valuable, given the country’s vulnerability to extreme weather events.
Impact of the Frontal System on Northern Luzon
The frontal system significantly influences the weather in Northern Luzon, resulting in scattered rain showers and thunderstorms. This meteorological phenomenon is characterized by the convergence of warm and cold air masses, which often leads to precipitation and turbulent weather. The implications of the frontal system on daily life are substantial, ranging from minor inconveniences to severe disruptions.
For the local populace, these weather conditions often translate into challenges for daily commuting and outdoor activities. Roads can become slippery and hazardous, increasing the likelihood of traffic accidents. Additionally, heavy rainfall can lead to flooding in low-lying areas, disrupting transportation and causing property damage. For agricultural communities, the impact is even more profound. Farmers rely heavily on predictable weather patterns to time their planting and harvesting cycles. The arrival of the frontal system can disrupt these cycles, potentially leading to crop damage and reduced yields.
Historically, Northern Luzon has experienced several significant weather events attributed to frontal systems. For instance, the heavy rains in November 2020 brought about by a frontal system led to widespread flooding in Cagayan Valley, affecting thousands of residents and causing extensive agricultural losses. Such events underscore the vulnerability of the region to frontal systems and the need for effective disaster preparedness and response strategies.
Apart from immediate impacts, the recurring nature of these weather patterns can have long-term economic repercussions. Persistent rainfall can erode soil quality, affecting future agricultural productivity. Moreover, the local fishing industry is also affected, as turbulent waters pose risks to small fishing boats and can lead to reduced fish catches.
Understanding the effects of the frontal system on Northern Luzon is crucial for developing adaptive strategies to mitigate its impacts. Enhanced weather forecasting and early warning systems can help communities prepare and respond more effectively to these weather events, ultimately safeguarding lives and livelihoods.
The Southwest Monsoon and Its Effects
The southwest monsoon, commonly referred to as ‘habagat’ in the Philippines, plays a pivotal role in shaping the country’s weather patterns. This seasonal wind system, which typically re-emerges between June and September, is characterized by its moist and warm air currents originating from the southwest. As it sweeps across the archipelago, ‘habagat’ significantly influences the climatic conditions, particularly in Southern Luzon and Northern Luzon.
During the southwest monsoon season, these regions often experience increased rainfall and humidity. The moist air carried by ‘habagat’ leads to heavy downpours, which can result in flooding and landslides, especially in low-lying and mountainous areas. The influx of moisture is also a critical factor in maintaining the agricultural productivity of these regions. Farmers rely on the predictable patterns of ‘habagat’ to plan their planting and harvesting schedules, ensuring that water-intensive crops such as rice receive adequate irrigation.
In contrast to other Southeast Asian countries, the Philippines’ geographic location and unique topography amplify the effects of the southwest monsoon. While nations like Thailand and Vietnam experience similar monsoonal patterns, the archipelagic nature of the Philippines allows ‘habagat’ to impact a more extensive range of local microclimates. This variation in weather can be attributed to the numerous islands and diverse landscapes that interact differently with the monsoon winds.
The significance of the southwest monsoon extends beyond agriculture. It also plays a crucial role in replenishing the country’s water reservoirs and sustaining its freshwater ecosystems. However, the intensity of ‘habagat’ can pose challenges, including disruptions to transportation and infrastructure due to severe weather conditions. Understanding and predicting the behavior of ‘habagat’ is therefore essential for disaster preparedness and mitigation efforts.
Overall, ‘habagat’ is a defining feature of the Philippines’ climate, bringing both opportunities and challenges. Its influence on weather patterns underscores the importance of seasonal monsoons in the region, highlighting the need for continuous research and monitoring to adapt to and harness the benefits of this natural phenomenon.
The Role of Easterlies in Philippine Weather
The term “easterlies” refers to trade winds that blow from the east toward the west, significantly influencing the weather patterns in various regions, including the Philippines. These easterlies originate over the expansive Pacific Ocean, carrying moisture and warmth as they traverse toward the archipelago. Their impact on the weather is particularly noticeable in areas such as Metro Manila, where they contribute to a distinct climate profile.
In the Philippines, the easterlies play a pivotal role in shaping the general weather conditions. They generally bring warm and humid air, leading to higher temperatures, especially during the summer months. This influx of warm air can also result in increased humidity levels, contributing to the overall discomfort experienced during these periods. Moreover, the easterlies can lead to relatively stable weather conditions, with fewer disturbances when compared to other seasonal wind patterns such as the southwest monsoon, known locally as “Habagat.”
The influence of easterlies is not unique to the Philippines. Similar wind patterns are observed in other tropical and subtropical regions around the globe. For instance, in the Caribbean and parts of Central America, the easterlies, also known as trade winds, have a comparable effect on the weather. These regions experience warm, moist air that influences their tropical climate, leading to consistent temperatures and frequent rainfall. The stability brought about by the easterlies in these regions is akin to what is observed in the Philippines, underscoring the global significance of these wind patterns.
Understanding the role of easterlies provides valuable insights into the climatic behavior of the Philippines. Their consistent presence and impact on temperature and humidity levels underscore the importance of these winds in maintaining weather stability. Comparisons with other global regions further highlight the universal nature of the easterlies’ influence, offering a broader perspective on their role in shaping weather patterns worldwide.
Localized Weather Phenomena: Isolated Downpours and Thunderstorms
Isolated downpours and thunderstorms are frequent occurrences in the Philippines, particularly during the wet season. These weather phenomena typically manifest in the afternoon or at night, driven by a combination of atmospheric instability, moisture content, and geographical factors. The confluence of warm, humid air and cooler air masses often leads to the development of convective cells, resulting in sudden and intense rainfall coupled with thunder and lightning.
The archipelagic nature of the Philippines, with its diverse topography, significantly influences these localized weather events. Coastal areas and mountainous regions are especially prone to experiencing isolated thunderstorms due to orographic lift, where moist air is forced upwards by the terrain, leading to condensation and precipitation. Additionally, urban heat islands—areas with higher temperatures due to human activities—can exacerbate the formation of thunderstorms in cities, causing sudden and heavy downpours that may lead to flash flooding.
The impacts of these localized weather events can be profound for both urban and rural communities. In urban areas, heavy rainfall can overwhelm drainage systems, resulting in waterlogged streets and disrupting daily activities. The risk of electrical hazards also increases with thunderstorms, necessitating caution. In rural regions, intense downpours can lead to soil erosion, landslides, and damage to crops, adversely affecting agriculture and local livelihoods.
Given the unpredictability of isolated downpours and thunderstorms, preparedness is crucial. Residents are advised to stay informed through reliable weather updates from the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical, and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA). Ensuring proper drainage around homes, securing outdoor objects that could be blown away by strong winds, and unplugging electrical appliances during a thunderstorm are essential safety measures. For those living in flood-prone areas, having an emergency kit with necessities such as water, food, and first-aid supplies can be lifesaving. By taking these precautions, communities can better mitigate the adverse effects of localized weather phenomena.
Weather Forecasting and Public Awareness
Accurate weather forecasting and heightened public awareness are crucial elements in mitigating the adverse effects of severe weather conditions in the Philippines. The Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA) plays a pivotal role in disseminating timely and accurate weather information to the public. Through a combination of modern technology and traditional communication channels, PAGASA ensures that the populace is well-informed about impending weather disturbances.
PAGASA employs a multi-faceted approach to communication, utilizing television, radio, and social media platforms to reach a broad audience. Regular updates and warnings are broadcasted, especially during typhoon season, to ensure that communities can take necessary precautions. Furthermore, PAGASA’s website and mobile applications provide real-time weather updates and forecasts, allowing individuals to access the information from virtually anywhere.
The role of media in weather communication is equally significant. Media outlets act as intermediaries, amplifying PAGASA’s messages to ensure they reach every corner of the country. This partnership is vital during emergencies when swift and widespread dissemination of information can save lives. For instance, during Typhoon Haiyan in 2013, the concerted efforts of PAGASA and various media entities were instrumental in the timely evacuation of thousands of residents, thereby minimizing casualties.
Internationally, best practices in weather forecasting and public safety offer valuable insights. Countries such as Japan and the United States have developed advanced meteorological systems and robust public awareness campaigns. Japan’s Meteorological Agency (JMA) utilizes a sophisticated network of observation stations and satellites, paired with comprehensive public education programs, to enhance community preparedness. Similarly, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) in the United States employs an integrated warning system that combines scientific data with effective public communication strategies.
Incorporating these international best practices can further enhance the effectiveness of weather forecasting and public awareness initiatives in the Philippines. By continuously improving communication strategies and leveraging technological advancements, PAGASA and other stakeholders can better protect communities from the devastating impacts of adverse weather conditions.
Conclusion and Future Weather Outlook
In our comprehensive exploration of the weather patterns in the Philippines, we have delved into the intricate dynamics that influence the nation’s climate. From the prevailing monsoon seasons to the impact of regional weather systems, it is evident that the Philippines experiences a diverse range of meteorological phenomena. The current weather conditions reflect a period of relative stability, characterized by the absence of tropical cyclones or low-pressure areas. This period offers a brief respite from the more tumultuous weather episodes that often occur in the region.
As we look ahead, the weather patterns for the coming days are expected to remain largely stable. Meteorological forecasts indicate a continuation of this calm phase, with no significant tropical disturbances on the horizon. However, it is crucial to recognize that the weather in the Philippines can be highly unpredictable. Sudden changes can occur, and it is essential for residents and visitors alike to stay informed through reliable weather sources.
Preparedness is key to mitigating the impact of any unexpected weather events. By staying updated with accurate weather information from trusted agencies, individuals can make informed decisions and take necessary precautions. This proactive approach ensures safety and minimizes disruptions to daily activities.
In conclusion, while the current outlook suggests a period of stable weather, the inherent variability of the Philippines’ climate necessitates continuous vigilance. Encouragingly, the absence of immediate weather threats provides a window of opportunity to focus on preparedness measures. By remaining informed and ready for any sudden changes, we can better navigate the complexities of the Philippines’ weather patterns.